More On: Google Cloud
Google Cloud offers developers access to its foundational models
Global Market Analysis and Forecast for Data Science and Machine Learning Platforms: Key Players, Regional Trends, and Future Outlook until 2029
Essential Machine Learning Knowledge for Data Scientists
Forecasting Machine Learning as a Service Market: Size, Segmentation, Parameters, and Projections through 2032
Deep Learning Innovations Fuel the Expansion of the Machine Learning Industry - Grand View Research, Inc.
Google Cloud made a significant announcement today, revealing a plethora of fresh AI-powered functionalities for its productivity tools. However, the company's latest release of APIs and tools for developers is equally intriguing - and arguably, even more compelling.
Aside from offering its vast language models via API access, Google has unveiled a new browser-based tool called MakerSuite, designed to streamline the process of building AI-driven applications utilizing the company's foundational models.
Furthermore, Google is introducing generative AI capabilities to its Vertex AI platform, enabling developers to construct and deploy machine learning models more efficiently. The tech giant has also launched its Generative AI App Builder service, which aims to assist developers in developing chat interfaces, digital assistants, bots, and customized search engines.
Similar to its latest AI tools in Workspace, these fresh features will initially be released to a limited number of developers and will only be accessible in Google's North American data centers. Some of the current customers utilizing these tools include Deutsche Bank, Mayo Clinic, and Toyota.
The PaLM API is the centerpiece of these new releases, and it has been a long-standing project for Google. However, the company describes the PaLM API as the primary channel for accessing its large language models. "This marks the first time we're providing new generative AI models to the developer community through a directly accessible API," according to Google Cloud CEO, Thomas Kurian.
Kurian explained that the new API offers developers an "incredibly intuitive way to start constructing with generative AI." He further stated that the API provides developers with access to foundational models, as well as the ability to fine-tune and supplement these models with their own data, and incorporate synthetic data into their dataset "to develop applications in a responsible and secure manner, to scale the applications for serving or inferencing, utilizing Google's infrastructure, and to generate cutting-edge embeddings."

Google has announced that it will offer an "efficient model in terms of size and capabilities" starting today, with additional models and sizes to be added in the near future. It's unclear why Google decided to use the name "PaLM" for this API instead of a more generic name, but the PaLM model will be accessible via this API for single-turn general-purpose applications such as text summarization and classification, as well as multi-turn conversations. A spokesperson for the company explained that PaLM was chosen for this initial release "because it performs exceptionally well for chat and text use cases." Potential candidates for additional models include LaMDA and MUM.
Google has also launched a low-code service called MakerSuite, which will be particularly useful for developers who don't want to get involved with the API. This service will be available exclusively to Trusted Testers and will provide access to two models: PaLM chat-bison-001 and PaLM text-bison-001. PaLM chat is designed to build chat-style, multi-turn applications, while PaLM text is optimized for single-turn input/output scenarios.
The objective of the MakerSuite service is to enable developers to provide examples to the tool that illustrate the type of results they are seeking. Subsequently, they can test these results and make them available as code. However, Google has not provided many details on how this service will operate in practice.
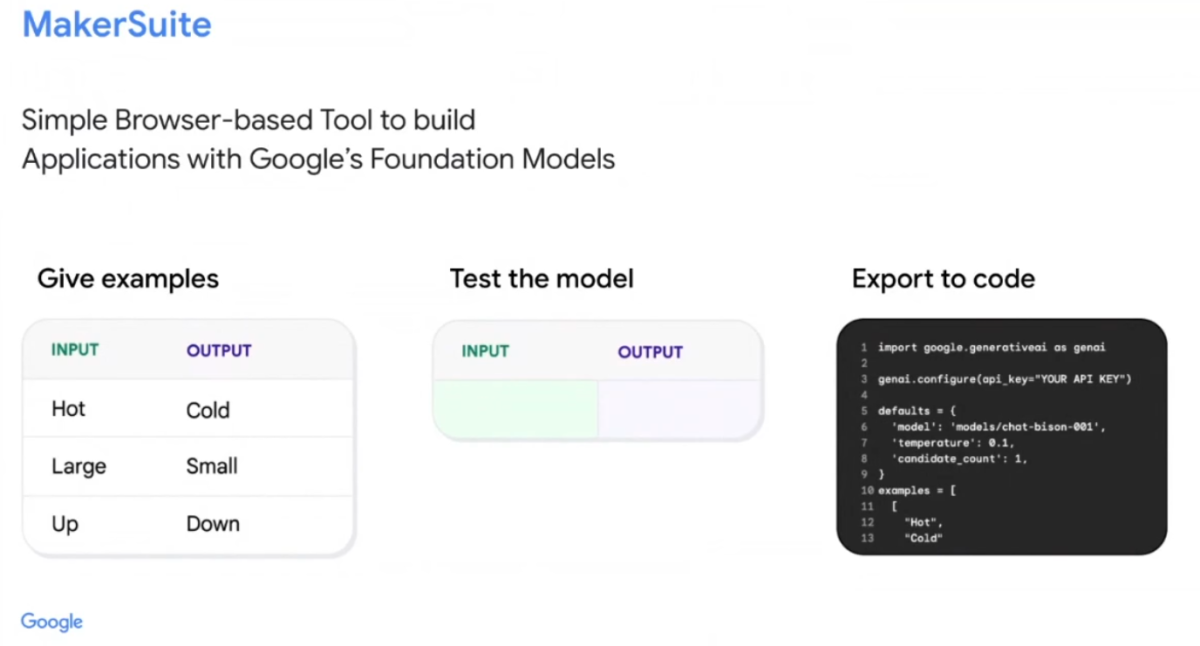
While Google mentioned MakerSuite briefly, it focused more on discussing Vertex AI and the Generative AI App Builder. Google has always provided an end-to-end service for developers to build their AI models and applications with Vertex AI. With this update, developers can now access foundation models for generating text and images. Google Cloud CEO Thomas Kurian stated that audio and video will be added to this platform over time. “The idea here is to let developers give a number of examples to the model and then quickly test these and make them available as code,” the company explained.
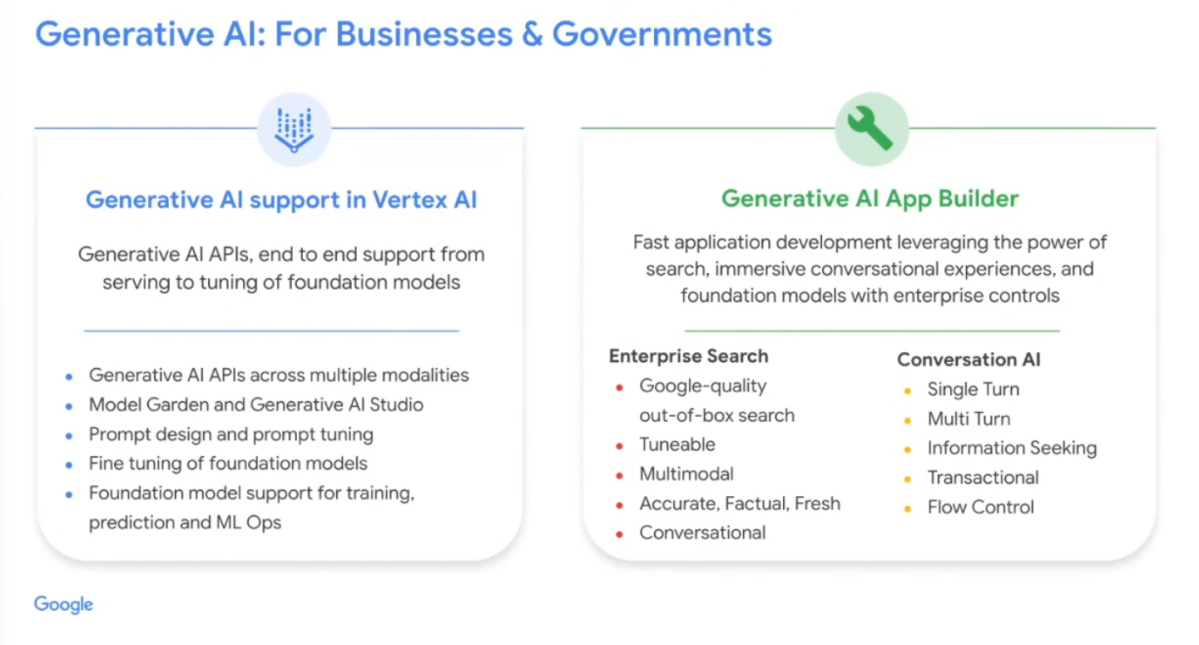
Google has also introduced a new service called the Generative AI App Builder, which enables developers and business users to create their own AI-powered chat interfaces and digital assistants based on their own data. According to Google Cloud CEO Thomas Kurian "The Generative AI App Builder is a fast application development environment that allows business users to work in concert with developers to leverage the power of search, conversation experiences, and foundation models while respecting enterprise controls".
To create this service, Google has combined its foundation models with its enterprise search capabilities and its conversation AI for building single- and multi-turn conversations. This service could be used to retrieve information, and with the right hooks into a company's APIs, it could be used to transact. Kurian emphasized that users will have control over the generative flow, allowing them to choose between giving the large language model control of the flow or using a more deterministic flow, such as in a customer service scenario where there is no risk of the model going off track.
In its various announcements, Google emphasized that the training data of a company will be kept confidential and not utilized to train the broader model. The company's focus is on business users who are interested in customizing the model for their use cases by incorporating their own data and/or fine-tuning it.
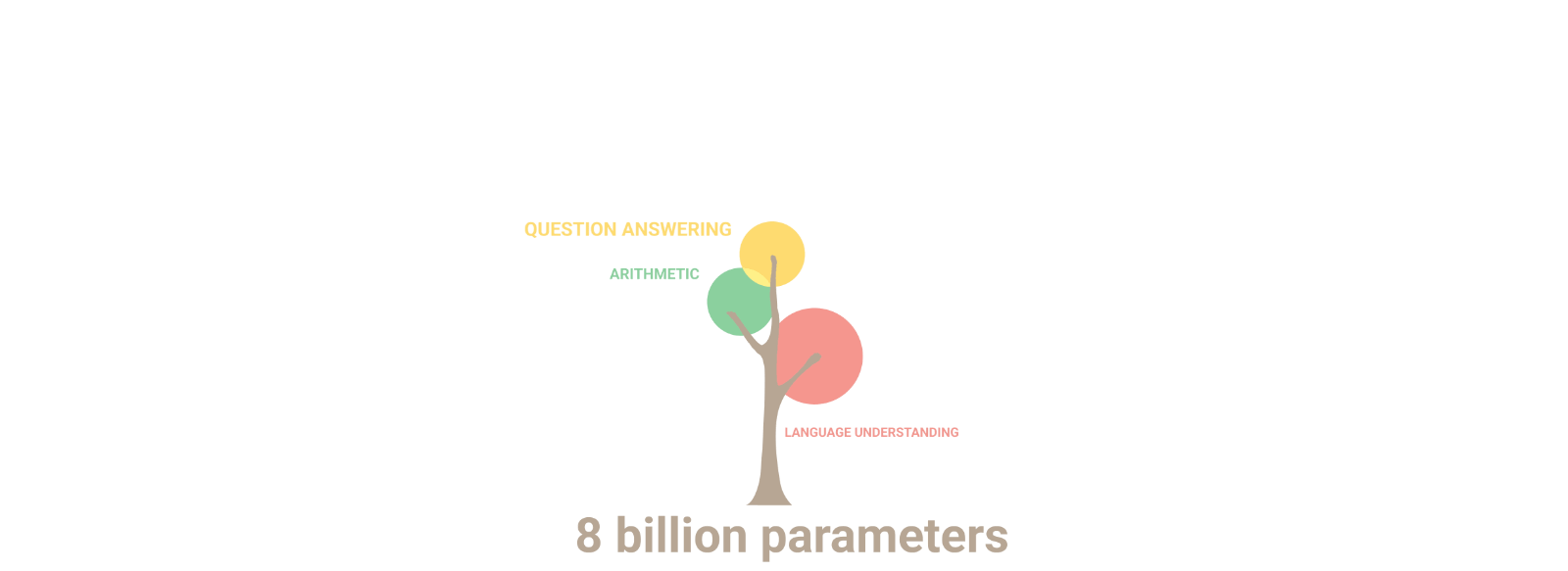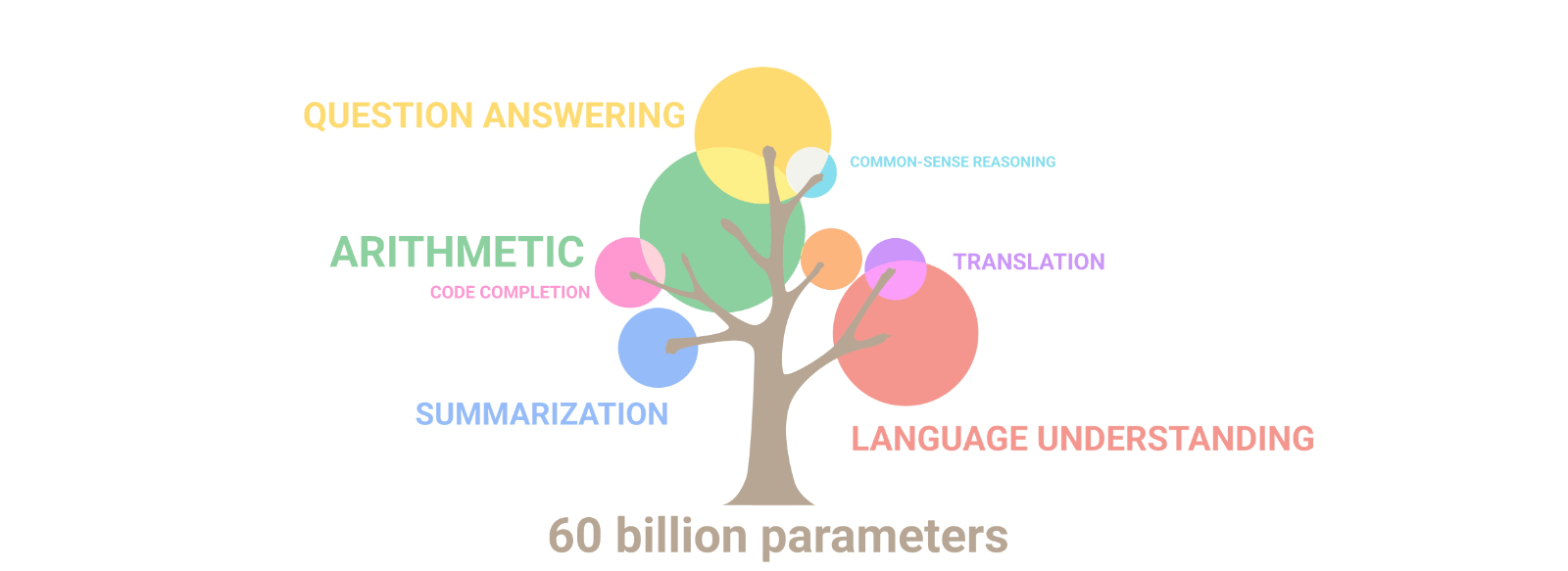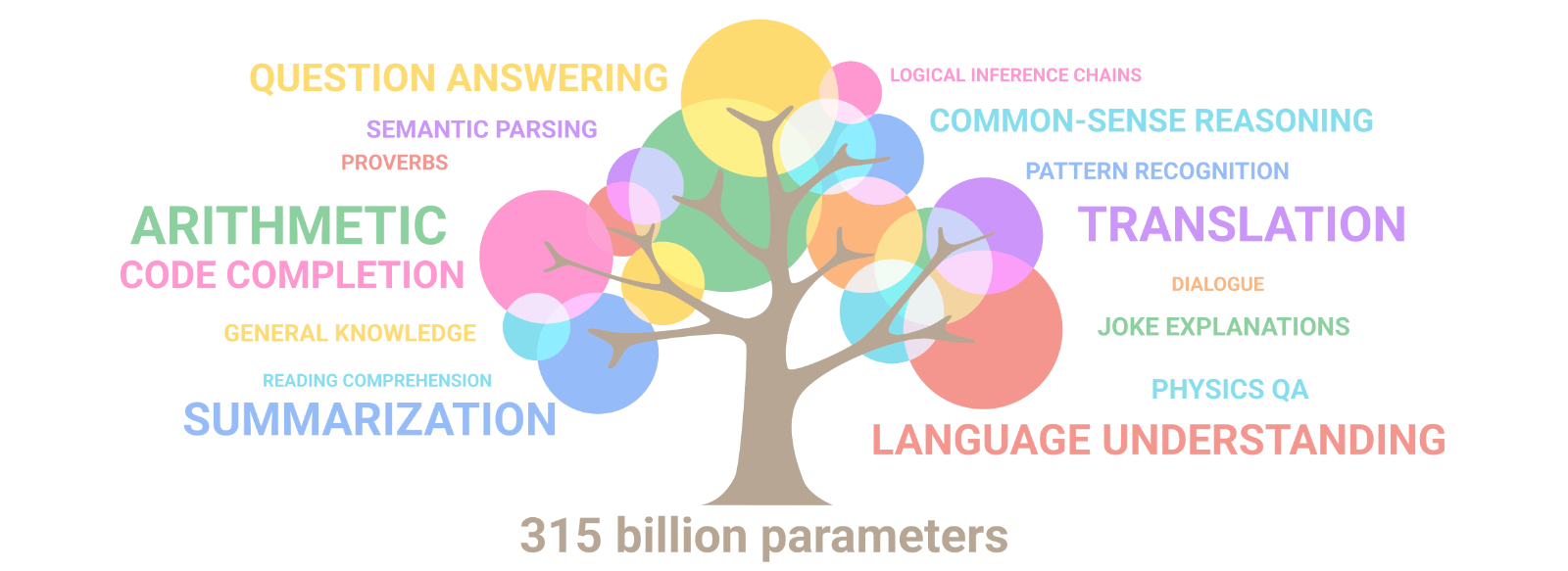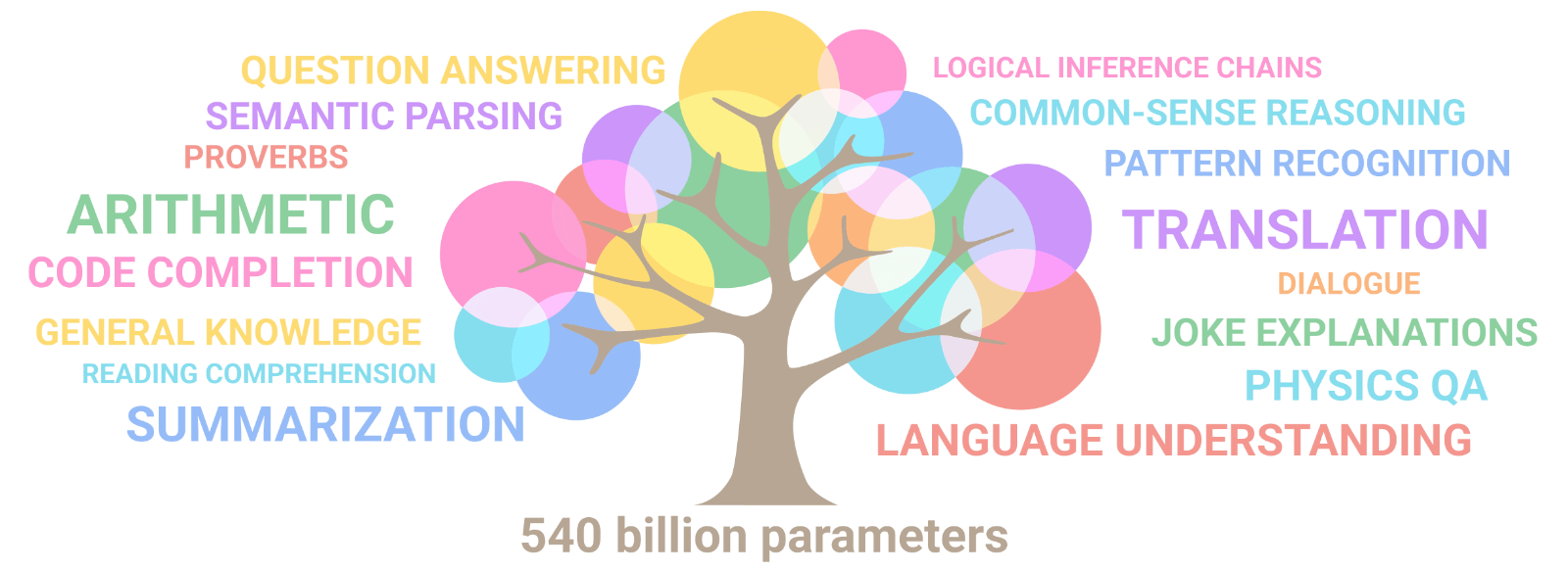
Google made several announcements related to AI at its virtual event. However, one thing that was notably missing was the public release of LaMDA, Google’s best-known model. Instead, the company chose to use the PaLM model as the foundation for its new services, which was first announced a year ago. PaLM is a large model with 540-billion parameters, significantly larger than OpenAI’s GPT3 with its 175 billion parameters. Google Research developed PaLM to generalize across domains and tasks while being highly efficient. While GPT3.5 is now in the market and GPT4 is expected to launch soon, it is not clear how PaLM will fare against these models in practice. However, Google claims that PaLM typically outperforms GPT3 in math questions, something that large language models are not necessarily best at. Additionally, the company noted that PaLM has shown strong performance across coding and natural language tasks in a single model, even though it has only 5% code in the pre-training dataset. It is worth noting that Google emphasized the privacy of a company’s training data and how it will not be used to train the broader model. The new services are mainly focused on business users who want to augment the model with their own data and/or tune it for their use cases.
Source Techrepublic












